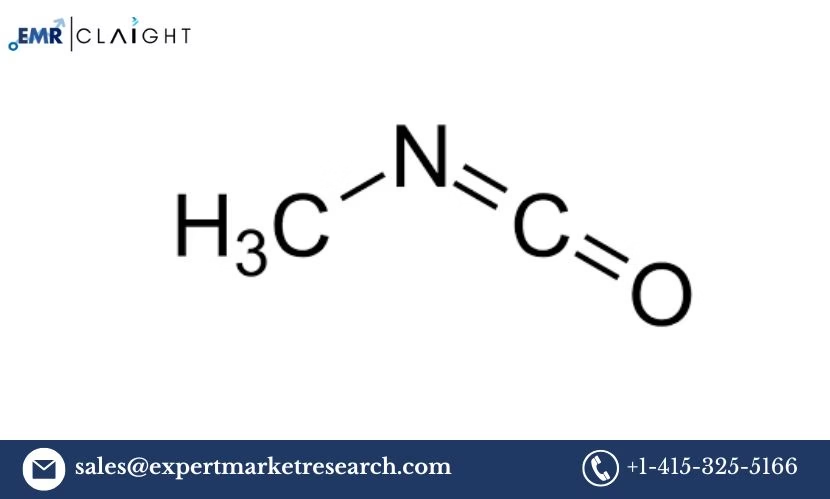
Introduction
The Methyl Isocyanate (MIC) Manufacturing Plant Project Report presents a comprehensive guide for establishing a production facility for methyl isocyanate, a critical chemical used in the manufacture of various industrial products, including pesticides, herbicides, and polymer foams. Methyl isocyanate plays a pivotal role in the production of isocyanates, which are vital intermediates for polyurethane production. This project report delves into the processes, technologies, market trends, financial considerations, regulatory aspects, and other essential factors for setting up a manufacturing plant for methyl isocyanate.
Market Overview
Methyl isocyanate is primarily used in the production of carbamate pesticides and polyurethanes, which are widely used across various industries, including agriculture, automotive, construction, and packaging. The global demand for methyl isocyanate is driven by increasing agricultural activities, the growth of the construction industry, and the rise in demand for polyurethane-based products.
Key Market Drivers:
- Agricultural Growth:
The global demand for pesticides, particularly carbamate pesticides, continues to rise with the increase in agricultural activities. This is one of the significant drivers for methyl isocyanate consumption. - Polyurethane Industry Expansion:
Methyl isocyanate is a key raw material in the production of polyurethane foams, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers. The expansion of the automotive, construction, and furniture industries fuels the demand for polyurethanes, thus boosting the demand for methyl isocyanate. - Rising Demand for Chemical Products:
Methyl isocyanate is also used in the production of specialty chemicals, which are in high demand for diverse applications in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and packaging. - Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements in chemical production processes are helping manufacturers increase efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of methyl isocyanate production.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Key Components
1. Market Analysis
This section provides a detailed overview of the methyl isocyanate market, which includes:
- Demand Analysis:
Understanding the growing demand for methyl isocyanate across various applications like pesticides and polyurethane products. - Competitive Landscape:
Identifying key players in the methyl isocyanate market, along with their production capacities, market share, and expansion strategies. - Regional Insights:
Insights into the demand for methyl isocyanate in various regions, with a focus on major consumers like North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe. - Growth Projections:
Analysis of projected market growth, including emerging trends such as increased demand from the construction and automotive industries.
2. Production Process of Methyl Isocyanate
The production of methyl isocyanate is a complex chemical process that requires strict control to ensure product quality and safety. The key steps include:
- Synthesis of Methyl Isocyanate:
Methyl isocyanate is typically synthesized by reacting methylamine with phosgene in the presence of a solvent such as dichloromethane. The chemical reaction is highly exothermic and requires careful temperature control. - Purification:
After the reaction, the crude methyl isocyanate is separated from the by-products and purified using distillation or other separation techniques. Purity levels of 99% or higher are typically required for industrial applications. - Storage and Handling:
Methyl isocyanate is highly toxic and volatile, necessitating specialized storage facilities. The plant must have airtight containers, proper ventilation, and safety mechanisms to prevent accidental leaks or exposure. - Packaging:
Once purified, methyl isocyanate is carefully packaged in appropriate containers. Special care is taken in handling and packaging to ensure that the chemical remains stable during transportation and storage.
3. Technology Requirements
To manufacture methyl isocyanate safely and efficiently, the plant needs specialized technologies and equipment:
- Reaction Vessels:
High-quality reaction vessels are essential for carrying out the chemical reaction between methylamine and phosgene. These vessels must be resistant to corrosion and able to withstand high temperatures and pressure. - Distillation Units:
Distillation units are necessary for purifying the methyl isocyanate. The distillation column separates the methyl isocyanate from any unreacted substances and by-products. - Safety Equipment:
Given the toxic nature of methyl isocyanate, the plant must be equipped with toxic gas detectors, emergency neutralization systems, and ventilation systems to ensure safety for workers and the environment. - Storage Tanks:
Specialized storage tanks designed to handle highly reactive and toxic chemicals are required to store methyl isocyanate safely before it is packaged for distribution.
4. Cost Analysis
The capital expenditure (CapEx) and operational expenditure (OpEx) are essential components of this section:
- Capital Expenditure:
This includes the cost of acquiring land, building infrastructure, and setting up the manufacturing plant. Investments in high-quality chemical reactors, distillation units, storage facilities, and safety systems are major cost components. - Operational Costs:
Ongoing operational costs include raw material procurement (methylamine and phosgene), utilities (electricity, water, etc.), labor costs, safety measures, and maintenance. - Packaging and Distribution Costs:
These costs encompass packaging materials, storage, and transportation. Given the hazardous nature of methyl isocyanate, special handling procedures add to distribution costs. - Profitability Analysis:
The report assesses the profitability of the project by estimating the production scale, market demand, and pricing strategies. A detailed break-even analysis will help determine the time required to recover the initial investment.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Methyl isocyanate manufacturing plants must adhere to several regulatory standards:
- Environmental Regulations:
The plant must comply with environmental impact assessments and ensure that emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants are minimized. - Safety Standards:
Due to the hazardous nature of methyl isocyanate, plants must follow strict safety protocols, including employee training on handling toxic chemicals and emergency response procedures. - Chemical Handling Certifications:
The plant must obtain certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management.
6. Sales and Distribution Strategy
To maximize revenue, manufacturers must implement an effective sales and distribution strategy:
- Direct Sales:
Manufacturers may choose to sell methyl isocyanate directly to large-scale chemical manufacturers or industrial customers. - Distributor Partnerships:
Establishing relationships with chemical distributors who have a network of clients can be an effective way to reach a broader market. - Global Expansion:
Given the high demand for methyl isocyanate in industries like agriculture and polyurethane production, expanding into international markets can increase profitability.
FAQ
1. What is methyl isocyanate used for?
Methyl isocyanate is primarily used in the production of pesticides, polyurethane foams, and other specialty chemicals.
2. How is methyl isocyanate produced?
Methyl isocyanate is synthesized by reacting methylamine with phosgene, followed by purification through distillation.
3. What are the safety concerns associated with methyl isocyanate?
Methyl isocyanate is highly toxic and volatile. Safety measures include specialized storage, toxic gas detectors, and emergency neutralization systems.
4. What are the key technologies required for methyl isocyanate production?
The production of methyl isocyanate requires reaction vessels, distillation units, safety equipment, and storage tanks.
5. What are the environmental concerns in methyl isocyanate manufacturing?
Manufacturing plants must manage hazardous chemical emissions and comply with environmental regulations to minimize the ecological footprint.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au